As a retired K-12 teacher and member of a community makerspace called Makersmiths, I volunteer as an educational liaison, working with families seeking opportunities for their children to become involved in STEM activities. One of Makersmiths initiatives is the KidWind-Virginia Challenge. During the 2018-2019 school year, I volunteered with two other Makersmiths members to sponsor two KidWind teams.
The teams learned about wind energy, how to design, create and test their blades on turbine stands. They learned to use multimeters and a Vernier Go Direct Sensor that uses Graphical Analysis software to determine their wind turbines’ energy production. At the spring 2019 KidWind-Virginia challenge event, the high school team won first place with their 3D printed blades and homemade generator producing the most energy and the middle school team earned two awards for their knowledge of wind energy initiatives, and for best documented blade design development.
 |
 |
Excited about their KidWind Challenge successes, our middle school students wanted to learn Tinkercad to design new blades and use 3D printers and a laser printer to construct blades for the 2020 wind turbine competition.
 |
 |
However, COVID-19 postponed the competition until spring 2021. We still held weekly meetings using Google Meet to offer advice as students completed their KidWind projects at home. I built the KidWind Challenge website to provide the students with information they needed to know about wind turbines. Since the middle school students also wanted to compete in the 2021 Kidwind Solar Structure Challenge, I built a solar structure website, too.
The students experimented with items such as solar panels, LEDs, switches, fans and water pumps found in their KidWind solar kits obtained from the JMU’s Center for the Advancement of Sustainable Energy (CASE) that sponsors KidWind-Virginia. The five middle school students eventually formed three teams that won first, second and third place awards in the middle school KidWind-VA 2021 Solar Structure Challenge. What were their projects?
 First place winners Connor, Caleb and Soren wanted to build a Kiosk solar project that contains a sound box. The sound box detects movement and plays a train sound whenever someone walks by it. The purpose of the sound is to catch the attention of that person and draw them back to the kiosk to read displayed information.
First place winners Connor, Caleb and Soren wanted to build a Kiosk solar project that contains a sound box. The sound box detects movement and plays a train sound whenever someone walks by it. The purpose of the sound is to catch the attention of that person and draw them back to the kiosk to read displayed information.
In order for sound box batteries to remain charged, the boys used three rechargeable batteries wired to two solar panels on a platform at the top of the kiosk. Tilted at an optimal angle to capture the direct sunlight during spring and summer, the panel can also be manually rotated to follow the sun.
 Second place winner Katie wanted to find a way to filter pond or stream water to use when watering plants. She created a water filtering system that uses a fish tank with a charcoal filter, two water pumps and three solar panels on a platform that can be adjusted to obtain the optimum angle to capture direct sunlight at different times of the year. The solar panels operate the two water pumps.
Second place winner Katie wanted to find a way to filter pond or stream water to use when watering plants. She created a water filtering system that uses a fish tank with a charcoal filter, two water pumps and three solar panels on a platform that can be adjusted to obtain the optimum angle to capture direct sunlight at different times of the year. The solar panels operate the two water pumps.
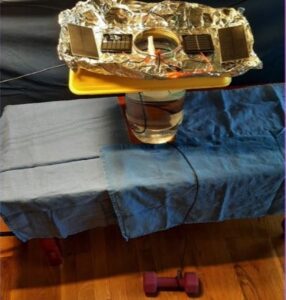 Third place winner Sofi figured out a way to use solar power to run an electrolysis system that separates hydrogen from oxygen in water. The hydrogen would power vehicles instead of using fossil fuels. She first used batteries to produce power to run her electrolysis system, then she switched to using solar power.
Third place winner Sofi figured out a way to use solar power to run an electrolysis system that separates hydrogen from oxygen in water. The hydrogen would power vehicles instead of using fossil fuels. She first used batteries to produce power to run her electrolysis system, then she switched to using solar power.
When thinking about what our students learned completing KidWind projects, many academic areas come to mind. Students used mathematics to measure when building projects and when completing their experiments, kept a journal to document the scientific data they were collecting, and wrote their procedures and results for judges to read. They had to collaborate to problem-solve and use their oral communication skills to create videos showing their projects in action. Most of all, our students developed maker skills and learned quite a bit about clean energy initiatives.
We would like to start a blog for VSTE members to share their makerspace initiatives. Perhaps you want to ask questions about how to establish a makerspace that ties into STEM initiatives? Let us know what you are thinking or wanting to ask!
Written by Diane D. Painter. Diane is a retired Fairfax County K-12 special education teacher. She teaches curriculum and instruction courses at Shenandoah University and volunteers as an educational liaison at Makersmiths, Inc., a non-profit makerspace in Loudoun County, VA. You can contact Diane through the Makersmiths website.




Diane, your continued desire to spark the creativity and imagination of our youth for deeper learning is so inspiring. I love the problem based learning that is occurring and the problem solving of real world, authentic problems while they are developing a passion for projects that can impact them for a lifetime but can also impact the global world. It can all start in Makersmiths where the “making” can make a big difference. You are inspirational. I love how you share your passion for learning.
This is definitively higher-level thinking and application. A great deal of problem solving and collaboration which many students need after a year of COVID- 19 restrictions. The cross-curricular application allows students to engage with the material on many levels and look at a problem on a larger scale versus simply content.